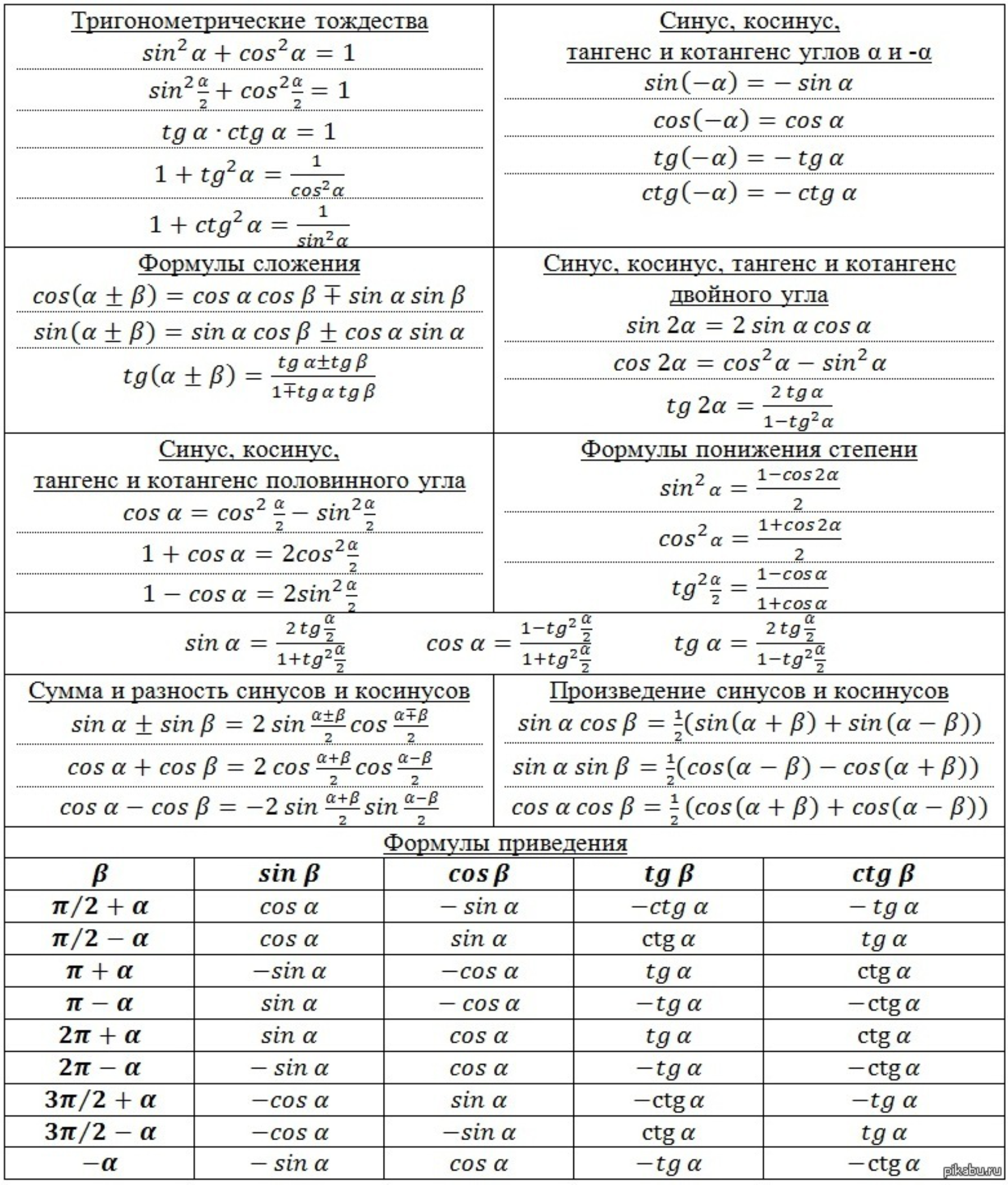
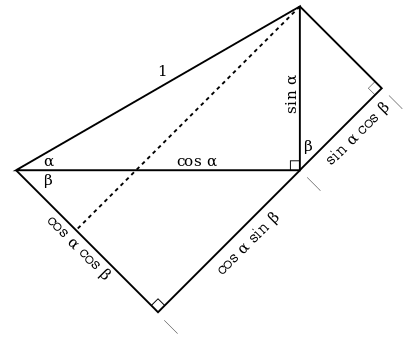
If sin alpha + sin beta =1/3 and cos alpha +cos beta =1/4, then what is the value of cos (alpha +beta)? - Quora
7, If cos (theta +iphi )=cos alpha +isin alpha , prove that(i) sin alpha =pm sin ^{2}theta (ii) sin alpha =pm sin h^{2} phi | Snapsolve
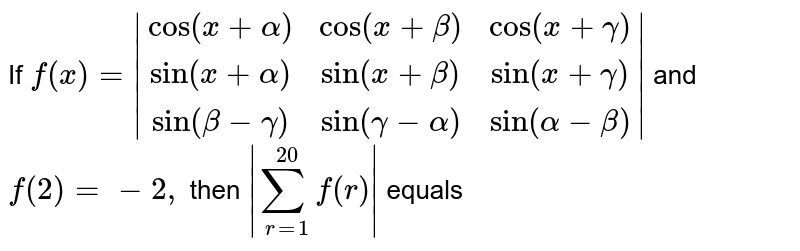
If f(x)=|(cos(x+alpha),cos(x+beta),cos(x+gamma)),(sin(x+alpha ),sin(x+beta),sin(x+gamma)),(sin(beta-gamma),sin(gamma-alpha),sin(alpha-beta))| and f(2)=6, then find 1/5 sum_(r=1)^25 f(r),

2D example for the functions (3.10), where S_1 = cos^2 \alpha, \hat S_1... | Download Scientific Diagram

Find \cos \alpha, given that \csc \alpha = -\frac{9}{2} and \alpha is in Quadrant IV. Show all work without a calculator. | Study.com

If cos ^{-1}(u+iv)=alpha +ibeta , prove that cos ^{2}alpha and cos h^{2}beta are the roots of the equation x^{2}-x(1+u^{2}+v^{2})+u^{2}=0. | Snapsolve

If sin A = 4/5,pi/2<A<pi and cos B = 5/13,3pi/2<B<2pi , find (i) sin (A + B) , (ii) cos (A - B) , (iii) tan (A - B)

Page 362 Qtn 3 Find out the distance between the following pairs of points a cos alpha a sin alpha and a cos beta a sin beta a m1 2 2 am1






![Ex 3.3, 12 (MCQ) - If A = [cos a -sin a sin a cos a], then A + A' = I Ex 3.3, 12 (MCQ) - If A = [cos a -sin a sin a cos a], then A + A' = I](https://d1avenlh0i1xmr.cloudfront.net/516a294a-c6cd-4b32-b98a-23cd61dd1ebc/slide47.jpg)